How To Register An Email Address On Android Emulator
The Android Emulator simulates Android devices on your computer then that you tin test your application on a diverseness of devices and Android API levels without needing to have each concrete device.
The emulator provides nigh all of the capabilities of a real Android device. Yous can simulate incoming phone calls and text messages, specify the location of the device, simulate unlike network speeds, simulate rotation and other hardware sensors, access the Google Play Shop, and much more.
Testing your app on the emulator is in some means faster and easier than doing so on a physical device. For instance, you can transfer data faster to the emulator than to a device connected over USB.
The emulator comes with predefined configurations for various Android phone, tablet, Article of clothing OS, and Android TV devices.
Lookout the following video for an overview of some emulator features.
You can employ the emulator manually through its graphical user interface and programmatically through the command line and the emulator console. For a comparison of the features bachelor through each interface, encounter Comparing of Android Emulator tools.
Requirements and recommendations
The Android Emulator has boosted requirements beyond the basic system requirements for Android Studio, which are described beneath:
- SDK Tools 26.1.1 or higher
- 64-flake processor
- Windows: CPU with UG (unrestricted guest) support
- HAXM 6.2.1 or later on (HAXM 7.two.0 or later recommended)
The employ of hardware dispatch has additional requirements on Windows and Linux:
- Intel processor on Windows or Linux: Intel processor with support for Intel VT-ten, Intel EM64T (Intel 64), and Execute Disable (XD) Bit functionality
- AMD processor on Linux: AMD processor with support for AMD Virtualization (AMD-Five) and Supplemental Streaming SIMD Extensions three (SSSE3)
- AMD processor on Windows: Android Studio 3.2 or higher and Windows 10 April 2018 release or higher for Windows Hypervisor Platform (WHPX) functionality
To work with Android 8.ane (API level 27) and college system images, an fastened webcam must have the capability to capture 720p frames.
Deprecation for 32-bit Windows systems
The Android Emulator was deprecated in June 2019 for 32-bit Windows systems. Back up for the 32-bit Windows emulator continues until June 2020, including critical issues fixes, simply no new features will exist added. If you are using the emulator on a 32-bit Windows system, you should programme to migrate to a 64-bit Windows system.
If you are using the emulator on a 32-bit Windows arrangement, you can use the SDK Managing director to install the latest version of the emulator for 32-bit Windows.
Install the emulator
To install the Android Emulator, select the Android Emulator component in the SDK Tools tab of the SDK Manager. For instructions, see Update your tools using the SDK Manager.
Android virtual devices
Each instance of the Android Emulator uses an Android virtual device (AVD) to specify the Android version and hardware characteristics of the simulated device. To finer test your app, you should create an AVD that models each device on which your app is designed to run. To create and manage AVDs, use the Device Manager.
Each AVD functions as an independent device, with its own private storage for user data, SD card, so on. By default, the emulator stores the user data, SD card data, and cache in a directory specific to that AVD. When you launch the emulator, it loads the user data and SD card data from the AVD directory.
Run an app on the Android Emulator
Yous tin run an app from an Android Studio project, or you can run an app that's been installed on the Android Emulator every bit you lot would run any app on a device.
To commencement the Android Emulator and run an app in your project:
- In Android Studio, create an Android Virtual Device (AVD) that the emulator can use to install and run your app.
-
In the toolbar, select the AVD that yous want to run your app on from the target device drop-downwardly menu.
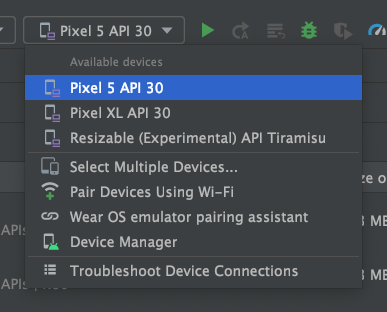
-
Click Run
 .
.If you receive an mistake or warning message at the elevation of the dialog, click the link to correct the problem or to get more information.
Some errors yous must ready before you tin keep, such every bit certain Hardware Accelerated Execution Director (Intel HAXM) errors.
For macOS, if y'all encounter a
Warning: No DNS servers founderror when starting the emulator, bank check to see whether you accept an/etc/resolv.conffile. If you don't have this file, enter the post-obit control in a terminal window:ln -s /private/var/run/resolv.conf /etc/resolv.conf
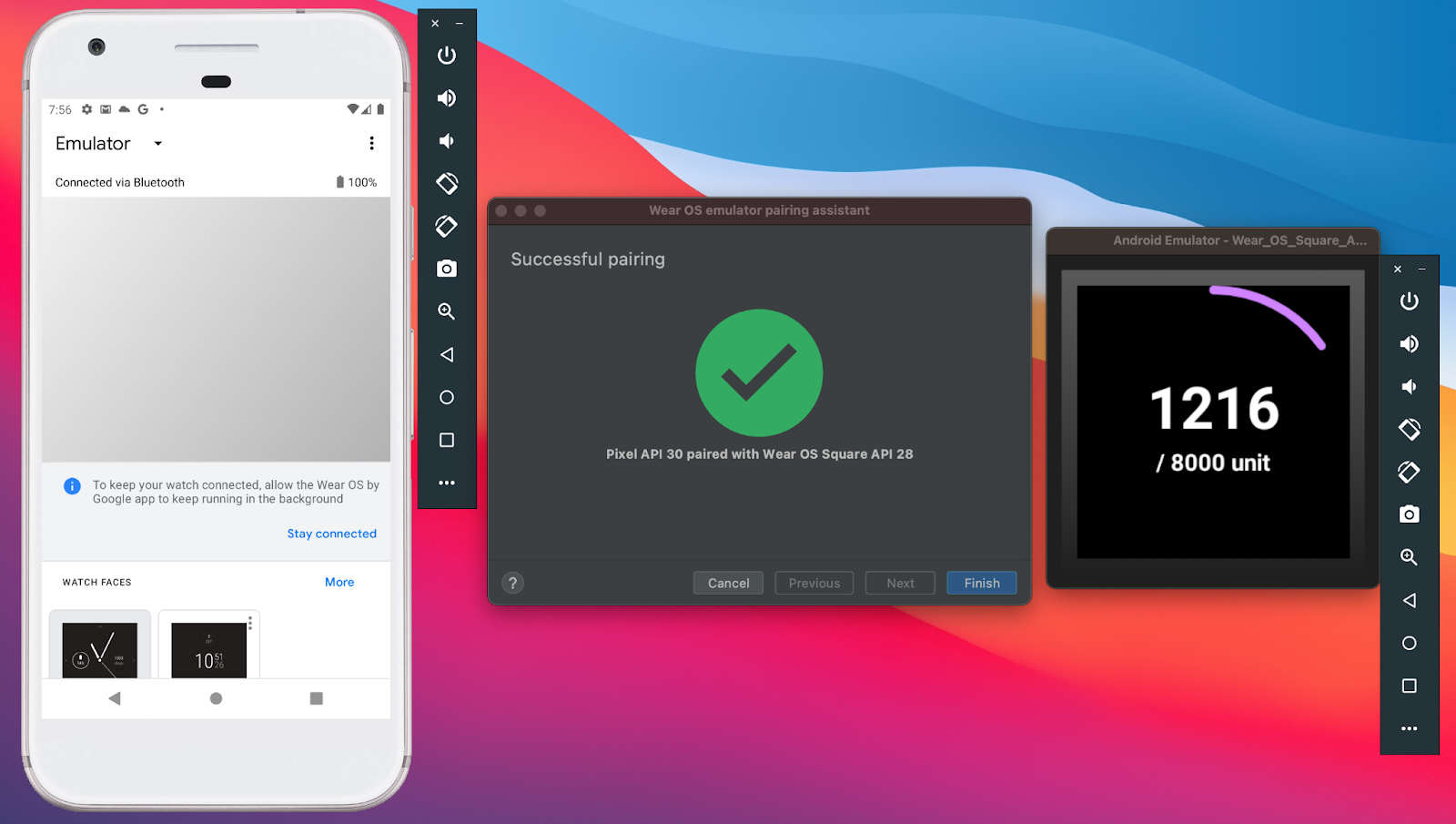
Habiliment OS pairing assistant
The Wear Os pairing assistant guides you stride-past-pace through pairing Wearable OS emulators with physical or virtual phones directly in Android Studio. The assistant can help y'all get the right Clothing OS Companion app installed on your phone and ready a connection between the ii devices. You can get started by going to the device dropdown > Wear OS Emulator Pairing Assistant.
Launch the Android Emulator without first running an app
To start the emulator:
-
Open the Device Manager.
-
Double-click an AVD, or click Run
 .
.The Android Emulator loads.
While the emulator is running, you tin run Android Studio projects and choose the emulator as the target device. Y'all can also drag ane or more APKs onto the emulator to install them, and then run them.
Run the Android Emulator directly in Android Studio
The Android Emulator runs directly within Android Studio by default. This allows you to conserve screen real estate, navigate speedily between the emulator and the editor window using hotkeys, and organize your IDE and emulator workflow in a single application window.
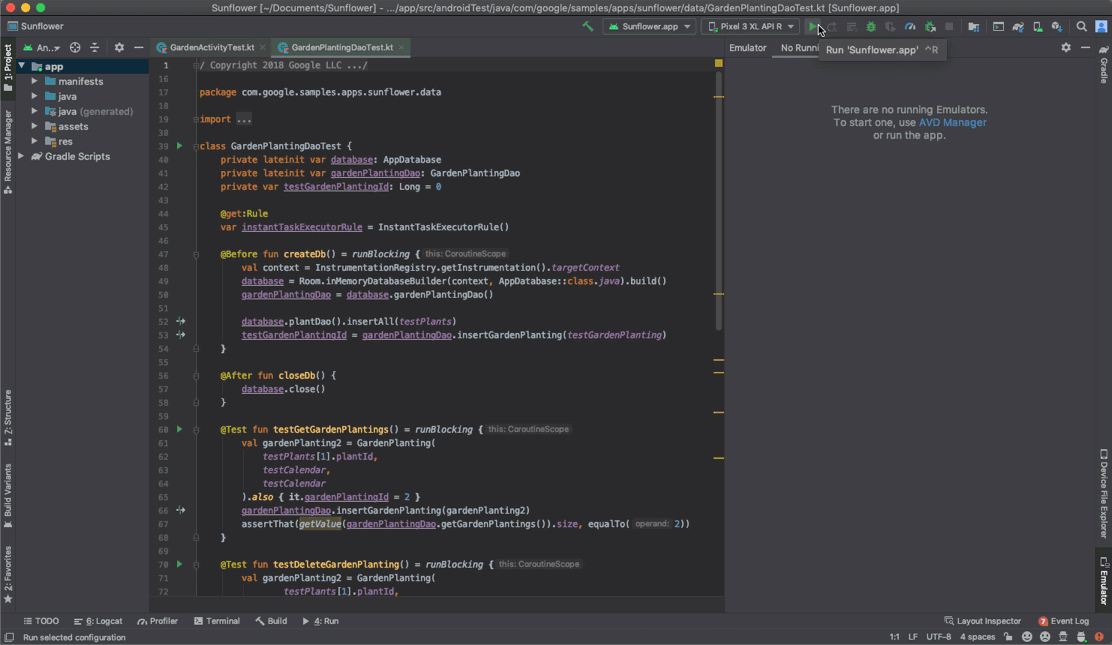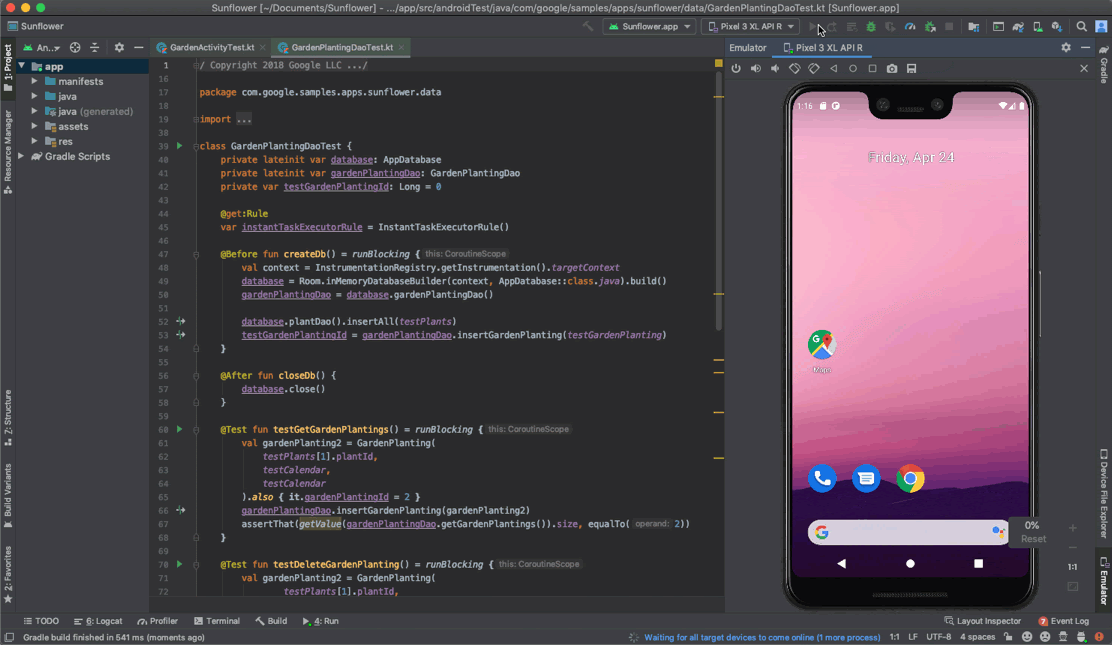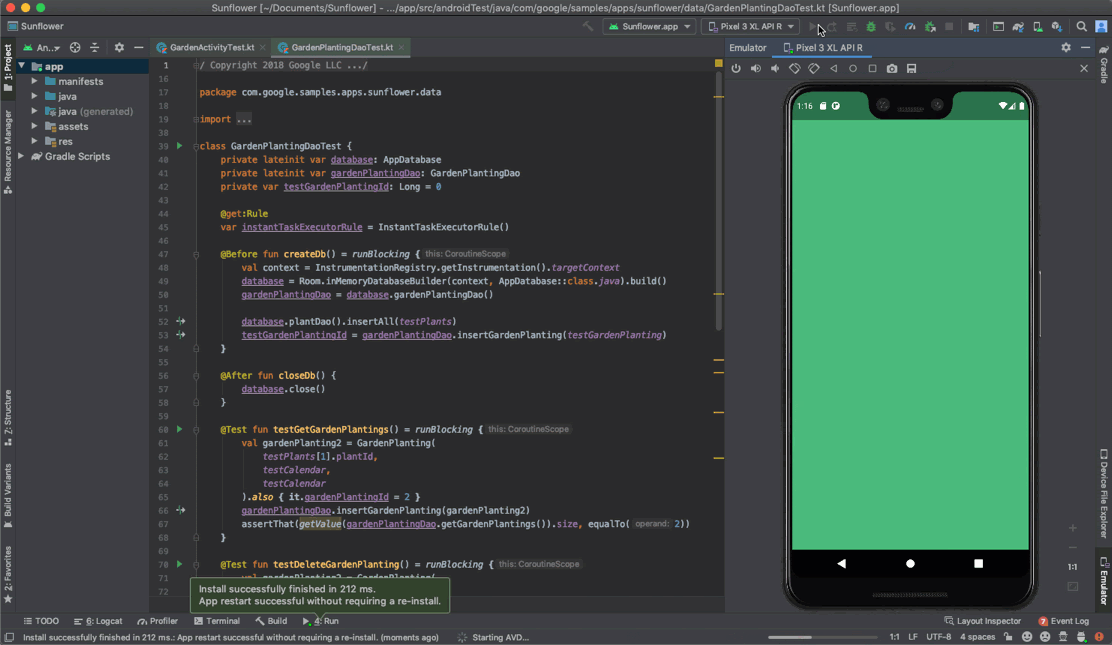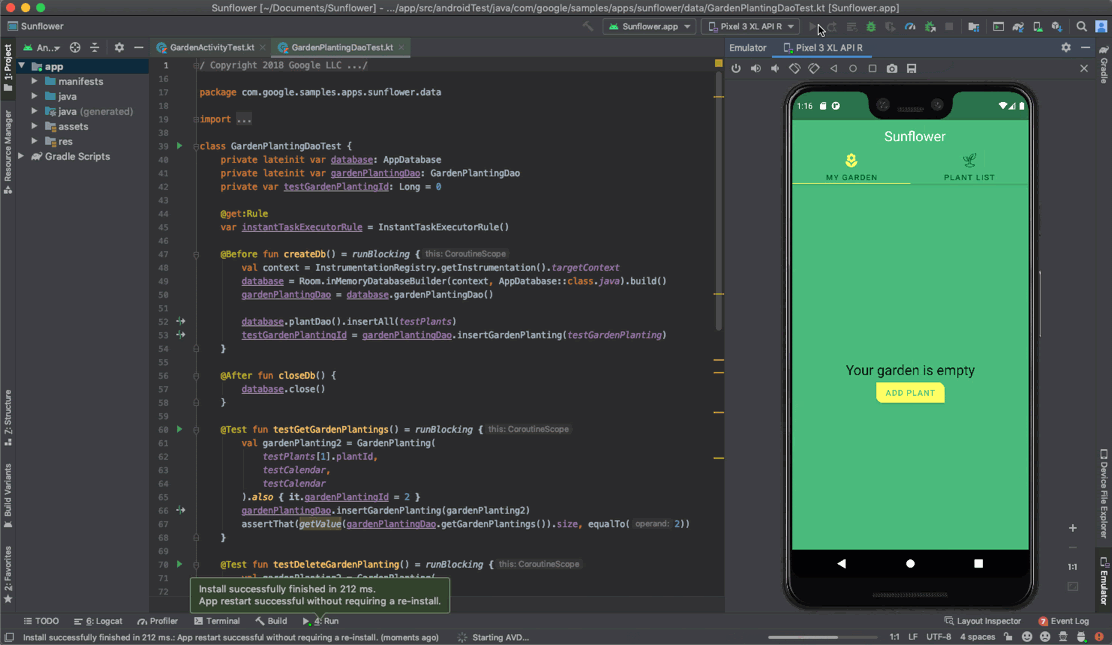
When the emulator is running, you'll have access to common emulator deportment like rotating, and extended control options similar navigation playback. To run the emulator in a separate window instead go to File > Settings > Tools > Emulator (Android Studio > Preferences > Tools > Emulator on macOS) and deselect Launch in a tool window.
Limitations
Currently, you can't use the emulator's extended controls when it'southward running in a tool window. If your evolution workflow depends heavily on the extended controls, proceed to employ the Android Emulator equally a standalone application. In improver, certain virtual devices—such as Android TV and foldable devices—can't be run in Android Studio because they have specialized UI requirements or important functions in the extended controls.
Install and add files
To install an APK file on the emulated device, drag an APK file onto the emulator screen. An APK Installer dialog appears. When the installation completes, you can view the app in your apps list.
To add together a file to the emulated device, drag the file onto the emulator screen. The file is placed in the /sdcard/Download/ directory. You tin view the file from Android Studio using the Device File Explorer, or discover information technology from the device using the Downloads or Files app, depending on the device version.
Snapshots
A snapshot is a stored image of an AVD (Android Virtual Device) that preserves the entire state of the device at the fourth dimension that it was saved – including Bone settings, application state, and user data. You tin can return to a saved organization state by loading a snapshot whenever you choose, saving yous the time of waiting for the operating system and applications on the virtual device to restart, every bit well as saving you the effort of bringing your app back to the state at which yous desire to resume your testing. Starting a virtual device by loading a snapshot is much like waking a physical device from a sleep state, every bit opposed to booting it from a powered-off state.
For each AVD, you tin can have one Quick Boot snapshot and whatever number of general snapshots.
The simplest way to accept reward of snapshots is to utilize Quick Boot snapshots: By default, each AVD is set to automatically save a Quick Boot snapshot on exit and load from a Quick Boot snapshot on offset.
The first time that an AVD starts, information technology must perform a common cold boot, just like powering on a device. If Quick Boot is enabled, all subsequent starts load from the specified snapshot, and the organization is restored to the state saved in that snapshot.
Snapshots are valid for the organization image, AVD configuration, and emulator features with which they are saved. When you make a change in any of these areas, all snapshots of the affected AVD become invalid. Whatever update to the Android Emulator, organization image, or AVD settings resets the AVD'south saved land, and so the next time you start the AVD, it must perform a cold kick.
Most controls for saving, loading, and managing snapshots are in the Snapshots and Settings tabs in the Snapshots pane in the emulator's Extended controls window.
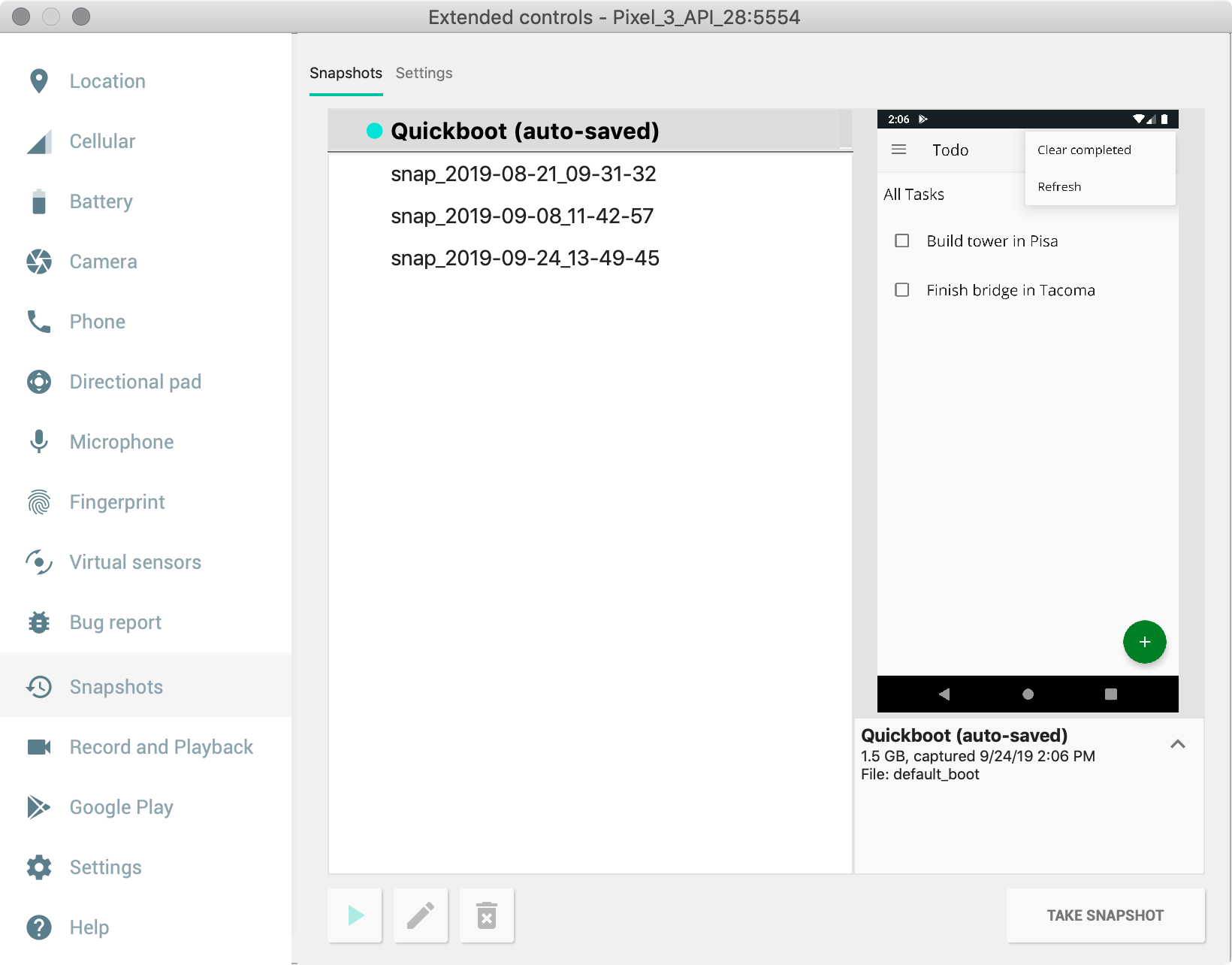
You can also control the Quick Kick options when starting the emulator from the command line.
Relieve Quick Boot snapshots
When you close an AVD, you can specify whether the emulator automatically saves a snapshot when you close. To command this behavior, proceed as follows:
- Open the emulator's Extended controls window.
- In the Snapshots category of controls, navigate to the Settings tab.
-
Use the Auto-save current state to Quickboot drop-downwards bill of fare to select one of the following options:
-
Yep: Always salve an AVD snapshot when you close the emulator. This is the default.
-
No: Don't save an AVD snapshot when you close the emulator.
-
Your selection applies only to the AVD that is currently open. You lot cannot salvage snapshots while ADB is offline (such equally while the AVD is still booting).
Save full general snapshots
Whereas you lot can simply have one Quick Boot snapshot for each AVD, yous can have multiple general snapshots for each AVD.
To save a general snapshot, open the emulator'south Extended controls window, select the Snapshots category, and click the Have snapshot push in the lower-right corner of the window.
To edit the proper noun and description of the selected snapshot, click the edit  button at the bottom of the window.
button at the bottom of the window.
Delete a snapshot
To manually delete a snapshot, open the emulator's Extended controls window, select the Snapshots category, select the snapshot, and click the delete  button at the bottom of the window.
button at the bottom of the window.
Y'all can as well specify whether you would like the emulator to automatically delete snapshots when they get invalid, such as when the AVD settings or emulator version modify. By default, the emulator will enquire you if you'd like for it to delete invalid snapshots. You tin modify this setting with the Delete invalid snapshots menu in the Settings tab of the Snapshots pane.
Load a snapshot
To load a snapshot at whatever time, open the emulator's Extended controls window, select the Snapshots category, choose a snapshot, and click the load  push button at the bottom of the window.
push button at the bottom of the window.
In Android Studio 3.two and college, each device configuration includes a Boot pick control in the avant-garde settings in the Virtual Device Configuration dialog with which you tin specify which snapshot to load when starting that AVD.
Disable Quick Kicking
If yous want to disable Quick Kick so your AVD always performs a common cold boot, do the following:
- Select Tools > Device Manager and click Edit this AVD
 .
. - Click Testify Advanced Settings and scroll down to Emulated Performance.
- Select Cold boot.
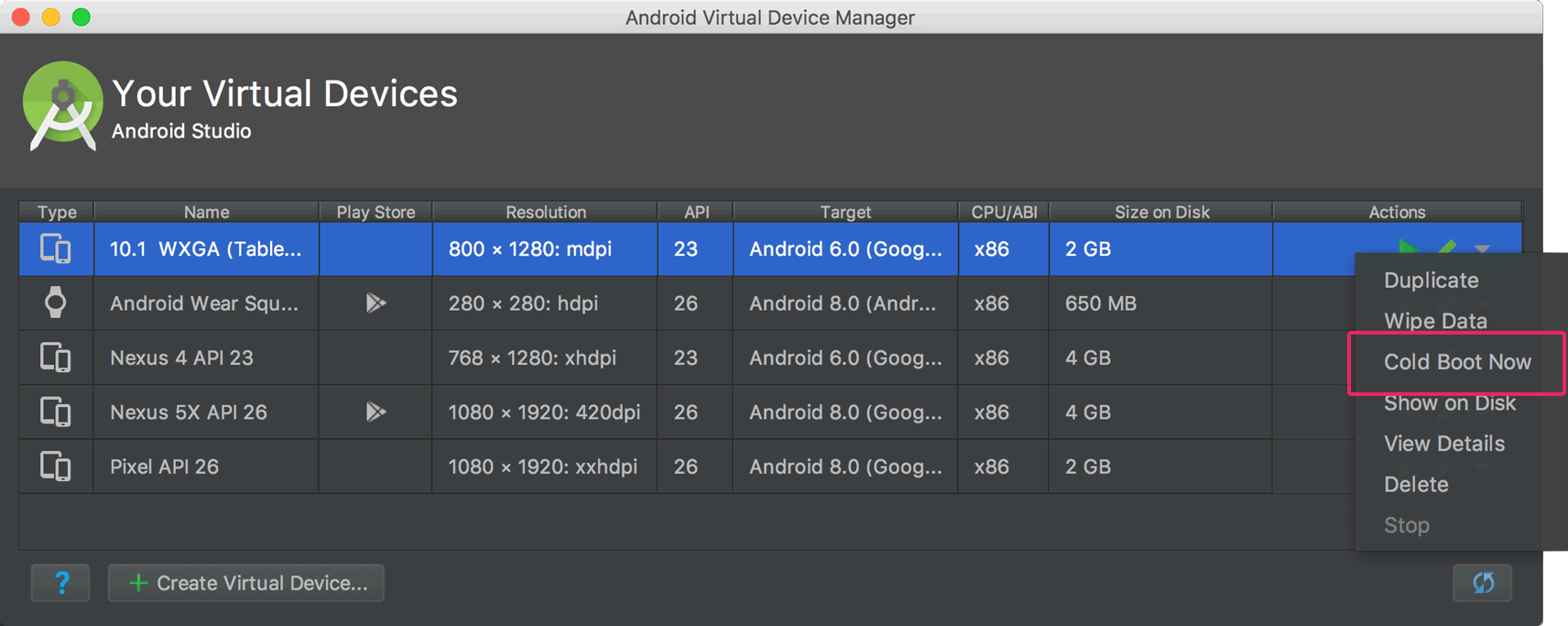
Cold boot once
Instead of disabling Quick Kicking completely, you lot can common cold boot simply once past clicking Cold Kicking Now from the AVD's driblet-down bill of fare in the Device Manager.
Snapshot requirements and troubleshooting
- Snapshots do non piece of work with Android 4.0.4 (API level 15) or lower.
- Snapshots do not work with ARM system images for Android 8.0 (API level 26).
- If the emulator fails to boot from a snapshot, select Cold Boot At present for the AVD in the Device Managing director and submit a bug report.
- Snapshots are not reliable when software rendering is enabled. If snapshots do not work, click Edit this AVD
 in the Device Manager and change Graphics to either Hardware or Automated.
in the Device Manager and change Graphics to either Hardware or Automated. - Loading or saving a snapshot is a retention-intensive operation. If you practise not have enough RAM free when a load or save operation begins, the operating system may swap the contents of RAM to the hard disk, which tin can greatly slow the operation. If you experience very boring snapshot loads or saves, yous may be able to speed these operations past freeing RAM. Closing applications that are not essential for your work is a skilful mode to free RAM.
Navigate the emulator screen
Use your computer mouse arrow to mimic your finger on the touchscreen; select bill of fare items and input fields; and click buttons and controls. Use your computer keyboard to type characters and enter emulator shortcuts.
Table 1. Gestures for navigating the emulator
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Swipe the screen | Betoken to the screen, printing and concur the primary mouse button, swipe across the screen, and then release. |
| Drag an item | Point to an item on the screen, press and hold the principal mouse button, move the item, then release. |
| Tap (impact) | Signal to the screen, printing the chief mouse button, and so release. For case, you could click a text field to start typing in information technology, select an app, or press a button. |
| Double tap | Point to the screen, printing the primary mouse button apace twice, then release. |
| Touch and hold | Point to an item on the screen, press the primary mouse push button, hold, and then release. For example, you could open options for an item. |
| Blazon | You tin type in the emulator by using your computer keyboard, or using a keyboard that pops up on the emulator screen. For case, y'all could type in a text field after you selected it. |
| | Pressing Control (Command on Mac) brings upwardly a pinch gesture multi-impact interface. The mouse acts as the commencement finger, and beyond the ballast betoken is the second finger. Drag the cursor to motility the get-go bespeak. Clicking the left mouse button acts like touching down both points, and releasing acts like picking both up. |
| Vertical swipe | Open a vertical card on the screen and use the scroll wheel (mouse cycle) to scroll through the carte items until you lot see the 1 y'all desire. Click the menu item to select it. |
Perform common actions in the emulator
To perform common deportment with the emulator, use the panel on the right side, every bit described in table ii.
Y'all can use keyboard shortcuts to perform many common actions in the emulator. For a complete list of shortcuts in the emulator, press F1 (Command+/ on Mac) to open the Help pane in the Extended controls window.
Tabular array two. Mutual actions in the emulator
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
Shut | Shut the emulator. |
Minimize | Minimize the emulator window. |
| Resize | Resize the emulator as you lot would any other operating system window. The emulator maintains an attribute ratio advisable for your device. |
Power | Click to turn the screen on or off. Click and hold to plough the device on or off. |
Book upwards | Click to view a slider command and turn the volume upwards. Click again to turn it up more, or use the slider control to alter the volume. |
Volume down | Click to view a slider control and plow the volume down. Click again to turn it down more, or use the slider control to change the volume. |
Rotate left | Rotate the device 90 degrees counterclockwise. |
Rotate correct | Rotate the device 90 degrees clockwise. |
Take screenshot | Click to accept a screenshot of the device. For details, see Screenshots. |
 | Click so the cursor changes to the zoom icon. To exit zoom manner, click the button again. Zoom in and out in zoom fashion:
To pan in zoom mode, agree Command (Command on Mac) while pressing the arrow keys on the keyboard. To tap the device screen in zoom mode, Command-click (Command-click on Mac). |
Dorsum | Render to the previous screen, or close a dialog box, an options menu, the Notifications console, or the onscreen keyboard. |
Home | Return to the Habitation screen. |
| Overview (Contempo Apps) | Tap to open up a list of thumbnail images of apps yous've worked with recently. To open an app, tap it. To remove a thumbnail from the list, swipe information technology left or right. This button isn't supported for Clothing Bone. |
Fold | For foldable devices, fold the device to display its smaller screen configuration. |
Unfold | For foldable devices, unfold the device to display its larger screen configuration. |
| Bill of fare | Printing Control+M (Command+M on Mac) to simulate the Menu button. |
More than | Click to access other features and settings, described in the next table. |
Screen recording
Y'all can record video and sound from the Android Emulator and save the recording to a WebM or animated GIF file.
The screen recording controls are in the Screen record tab of the Extended Controls window.
Tip: You tin can also open the screen recording controls by pressing Command + Shift + R (Command + Shift + R on Mac).
To begin screen recording, click the Start recording button in the Screen record tab. To stop recording, click Cease recording.
Controls for playing and saving the recorded video are at the bottom of the Screen record tab. To save the video, choose WebM or GIF from the card at the bottom of the tab and click Salve.
Y'all can also tape and save a screen recording from the emulator using the following control on the command line:
adb emu screenrecord start --time-limit ten [path to salve video]/sample_video.webm
Screenshots
To have a screenshot of the virtual device, click the Take screenshot  button.
button.
The emulator creates a PNG file with the name Screenshot_yyyymmdd-hhmmss.png using the year, month, day, hour, minute, and second of the capture. For case, Screenshot_20160219-145848.png.
By default, the screenshot is saved on your computer desktop. To change the location to which screenshots are saved, use the Screenshot save location control in the Settings category in the emulator'south Extended controls window.
You can as well take screenshots from the command line with either of the following commands:
-
screenrecord screenshot [destination-directory] -
adb emu screenrecord screenshot [destination-directory]
Camera support
The emulator supports the use of basic camera functionality on your virtual device for earlier Android versions. Android 11 and higher supports the following additional Android Emulator camera capabilities:
- RAW capture
- YUV reprocessing
- Level 3 devices
- Logical photographic camera support
- Emulating sensor orientation by using information from the sensor manager
- Applying video stabilization by reducing handshake frequency
- Applying border enhancement by removing the upscaling normally done in the YUV pipeline
- Concurrent cameras
Virtual scene camera and ARCore
You can use the virtual scene camera in a virtual environment to experiment with augmented reality (AR) apps made with ARCore.
For information on using the virtual scene camera in the emulator, encounter Run AR apps in Android Emulator.
When using the emulator with a camera app, you can import an image in PNG or JPEG format to exist used within a virtual scene. To choose an image for use in a virtual scene, click Add together epitome in the Camera > Virtual scene images tab in the Extended controls window. This feature tin can be used to import custom images such equally QR codes for utilise with any camera-based app. For more information, meet Add Augmented Images to the scene.
Test common AR actions with macros
Y'all can greatly reduce the time it takes to test mutual AR actions past using the preset macros in the emulator. For example, y'all can use a macro to reset all the device's sensors to their default state.
Before using macros, follow the steps in Run AR apps in Android Emulator to ready the virtual scene camera for your app, run your app on the emulator, and update ARCore. And so, follow these steps to use emulator macros:
- With the emulator running and your app continued to ARCore, click More
 in the emulator panel.
in the emulator panel. - Select Record and Playback > Macro Playback.
-
Cull a macro that yous want to employ, then click Play.
During playback, you can interrupt a macro by clicking Stop.
Extended controls, settings, and help
Use the extended controls to send data, modify device backdrop, control apps, and more. To open the Extended controls window, click More  in the emulator console.
in the emulator console.
You tin can apply keyboard shortcuts to perform many of these tasks. For a consummate listing of shortcuts in the emulator, printing F1 (Command+/ on Mac) to open up the Assist pane.
Table 3. Extended controls details
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Location | The emulator lets yous simulate "my location" information: the location where the emulated device is currently located. For case, if you click My Location Controls for the device's location information are organized under two tabs: Single points and Routes. Single points In the Unmarried points tab, you tin can use the Google Maps webview to search for points of involvement, just as you would when using Google Maps on a telephone or in a browser. When you search for (or click on) a location in the map, y'all tin can salvage the location by selecting Save indicate well-nigh the bottom of the map. All of your saved locations are listed on the right side of the Extended controls window. To set the emulators location to the location you lot have selected on the map, click the Gear up location button near the lesser right of the Extended controls window. Routes Similar to the Single points tab, the Routes tab provides a Google Maps webview that you tin can utilise to create a route between 2 or more locations. To create and relieve a route, do the following:
To simulate the emulator post-obit the route you saved, select the route from the list of Saved routes and click Play route near the bottom right of the Extended controls window. To stop the simulation, click End route. To continuously simulate the emulator following the specified road, enable the switch adjacent to Echo playback. To modify how quickly the emulator follows the specified route, select an pick from the Playback speed dropdown. Import GPX and KML data To utilise geographic data from a GPS exchange format (GPX) or Keyhole Markup Linguistic communication (KML) file:
The speed defaults to the Delay value (Speed 1X). You tin can increase the speed by double (Speed 2X), triple (Speed 3X), and then on. |
| Displays | The emulator allows you to deploy your app to multiple displays, which back up customizable dimensions and can help you test apps that support multi- window and multi- display. While a virtual device is running, you tin can add upwards to two additional displays as follows:
|
| Cellular | The emulator lets you simulate various network conditions. You tin can approximate the network speed for different network protocols, or y'all can specify Full, which transfers data as quickly as your computer allows. Specifying a network protocol is always slower than Full. You tin also specify the voice and data network status, such as roaming. The defaults are set in the AVD. Select a Network type:
Select a Point strength:
Select a Vox status, Data status, or both:
|
| Battery | Y'all can simulate the battery properties of a device to encounter how your app performs under different conditions. To select a Accuse level, use the slider control. Select a Charger connection value:
Select a Bombardment health value:
Select a Battery status value:
|
| Phone | The emulator lets you lot simulate incoming telephone calls and text messages. To initiate a phone call to the emulator:
To send a text message to the emulator:
|
| Directional Pad | If the AVD has the directional pad enabled in the hardware profile, you can use the directional pad controls with the emulator. Still, non all devices tin support the directional pad; for example, an Android sentry. The buttons simulate the following actions:  |
| Fingerprint | This control can simulate 10 unlike fingerprint scans. You lot can use it to test fingerprint integration in your app. This feature is disabled for Android 5.1 (API level 22) and lower, and for Article of clothing OS. To simulate a fingerprint scan on the virtual device:
|
| Virtual sensors > Accelerometer | This command lets you test your app against changes in device position, orientation, or both. For example, you can simulate gestures such as tilt and rotation. The accelerometer doesn't rail the accented position of the device: information technology but detects when a alter is occurring. The control simulates the way accelerometer and magnetometer sensors would respond when you motility or rotate a existent device. You lot must enable the accelerometer sensor in your AVD to apply this control. The command reports The command too reports To rotate the device around the ten, y, and z axes, select Rotate and do 1 of the post-obit:
See Calculating the device's orientation for more information nearly how yaw, pitch, and curl are calculated. To move the device horizontally (x) or vertically (y), select Motion and do one of the following:
To position the device at 0, 90, 180, or 270 degrees:
Equally you accommodate the device, the Resulting values fields alter appropriately. These are the values that an app can access. For more data nigh these sensors, meet Sensors overview, Movement sensors, and Position sensors. |
| Virtual sensors > Additional sensors | The emulator can simulate various position and environment sensors. It lets you lot adjust the following sensors and so y'all can exam them with your app:
For more information about these sensors, see Sensors overview, Position sensors, and Environment sensors. |
| Snapshots | Meet Snapshots. |
| Screen tape | See Screen recording. |
| Settings > General |
|
| Settings > Proxy | By default, the emulator uses the Android Studio HTTP proxy settings, merely this screen allows you to manually ascertain an HTTP proxy configuration for the emulator. For more than information, see Using the emulator with a proxy. |
| Settings > Advanced |
|
| Help > Keyboard Shortcuts | This pane provides a consummate list of keyboard shortcuts for the emulator. To open this pane while working in the emulator, press F1 (Command+/ on Mac). For the shortcuts to work, the Send keyboard shortcuts option in the General settings pane must be fix to Emulator controls (default). |
| Help > Emulator Help | To go to the online documentation for the emulator, click Documentation. To file a issues confronting the emulator, click Send feedback. For more information, see how to report emulator bugs. |
| Help > About | See which adb port the emulator uses, as well equally the Android and emulator version numbers. Compare the latest bachelor emulator version with your version to determine if you accept the latest software installed. The emulator serial number is emulator- adb_port, which you can specify equally an adb command line selection, for instance. |
Wi-Fi
When using an AVD with API level 25 or higher, the emulator provides a imitation Wi-Fi admission betoken ("AndroidWifi"), and Android automatically connects to it.
You can disable Wi-Fi in the emulator by running the emulator with the command-line parameter -characteristic -Wifi.
Limitations
The Android Emulator doesn't include virtual hardware for the post-obit:
- Bluetooth
- NFC
- SD card insert/eject
- Device-attached headphones
- USB
The watch emulator for Wear Bone doesn't provide the Overview (Contempo Apps) push button, D-pad, and fingerprint sensor.
How To Register An Email Address On Android Emulator,
Source: https://developer.android.com/studio/run/emulator
Posted by: whitneypriew1941.blogspot.com


 in Google Maps and then send a location, the map shows it.
in Google Maps and then send a location, the map shows it. 
0 Response to "How To Register An Email Address On Android Emulator"
Post a Comment